Setup MyLVS
Setup mySQL
At the very step we need to setup the database with all the required tables, please use the import script mylvs.sql to do so.
You will find the script within the archive or on your disk in: /var/www/mylvs/templates/mysql_data/mylvs.sql
mysql -u root -p < /var/www/mylvs/templates/mysql_data/mylvs.sql
You may also see: Create the Database and the Users
Setup Apache
Copy the configuration to your Apache Webserver:
cp /var/www/mylvs/templates/etc/apache2/sites-available/mylvs.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/
Optional copy the Webservice configuration to your Apache Webserver:
cp /var/www/mylvs/templates/etc/apache2/sites-available/ws.mylvs.foo.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/
Verify the configuration and enable it with a2ensite:
a2ensite ws.mylvs.foo.conf
Optional verify the configuration and enable it with a2ensite:
a2ensite mylvs.conf
Restart Apache
service apache2 restart
Add a demo account to apache, this will be the login through the browser, note that this step is required:
root@mylvs01:/# htpasswd -c /var/www/mylvs/wwwroot/.htpasswd.users demo
Login to myLVS
Depending on your client OS you may add a hostheader to your host file, to do this type
- Linux
# vi /etc/hosts
- Windows (Administrator command shell)
notepad c:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
Add:
192.168.x.y mylvs.foo
- Note: The Windows DNS Cache requires a reload:
ipconfig/flushdns
Navigate your prefered browser to mylvs.foo, login using demo, demo.
You should see a screen similar the this:
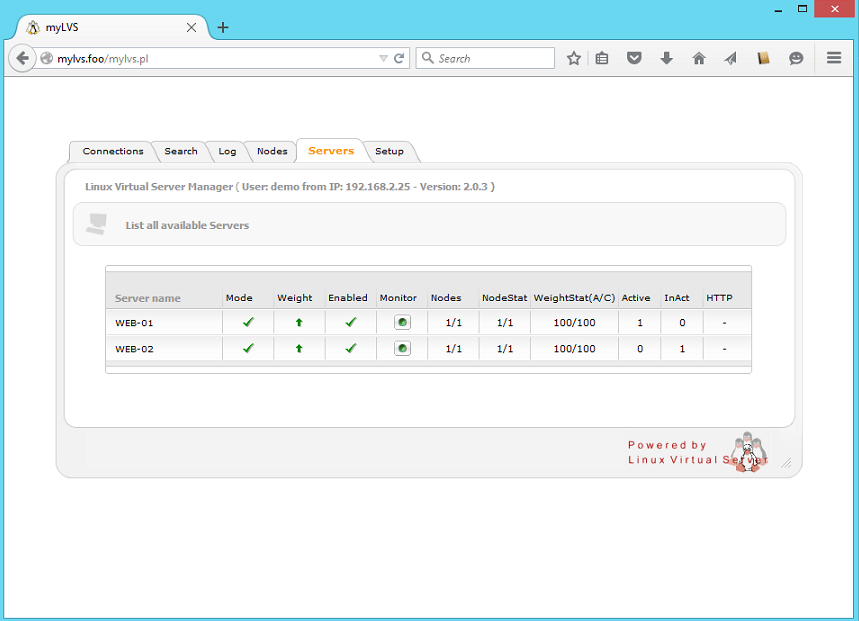
Note: To setup a fresh configuration you could easily setup the node and servers through the setup and begin then from scratch.
Automatic load of myLVS setting
To automatic load the myLVS configuration it is requires to setup sysmctl which comes new with Debian 8.
This configuration will start on boot only using the type oneshot, it is very important to load this after mysql.service
Create File: /etc/systemd/system/mylvs-init.service
Add:
[Unit] Description=myLVS Startup Script After=network.target auditd.service mysql.service [Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/usr/bin/perl /var/www/mylvs/mylvsinit.pl -a [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
- First status
root@mylvs01:/systemctl status mylvs-init.service mylvs-init.service - myLVS Startup Script Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/mylvs-init.service; disabled) Active: inactive (dead)
- Enable: systemctl enable mylvs-init.service
Output:
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mylvs-init.service to /etc/systemd/system/mylvs-init.service.
- Reload (optional): systemctl daemon-reload
- Reboot to test
- Live Status
root@mylvs01:/home/demo# systemctl status mylvs-init.service mylvs-init.service - myLVS Startup Script Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/mylvs-init.service; enabled) Active: inactive (dead) since Mon 2015-08-17 14:53:48 EDT; 1min 38s ago Process: 933 ExecStart=/usr/bin/perl /var/www/mylvs/mylvsinit.pl -a (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 933 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Automatic load of myLVS Monitor setting
Create File: /etc/systemd/system/mylvsmon.service
Add:
[Unit] Description=myLVS Monitor After=network.target auditd.service mysql.service [Service] ExecStart=/var/www/mylvs/mylvsmon.pl ExecStop=/usr//bin/killall -9 mylvsmon.pl KillMode=process RemainAfterExit=yes [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Note: The above has been tested on Debian 8/9
To manage use:
- Enable: systemctl enable mylvs-init.service
- Reload (optional): systemctl daemon-reload